Glass to Metal Sealing Solutions Using Ceramic Steatite Insulators
Release time:2026-01-15
Glass to metal sealing is a critical technology enabling reliable electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and long-term hermeticity in demanding industrial environments. By integrating ceramic steatite insulators into glass-to-metal seal systems, manufacturers can achieve unmatched hermetic seals with improved thermal stability, electrical insulation, and cost efficiency. This article explores the fundamentals, processes, applications, and future trends of glass to metal sealing technology, with a practical focus on ceramic steatite-based solutions and real-world manufacturing considerations.
Fundamentals of Glass to Metal Sealing
-Principles of glass to metal sealing
-Types of glass to metal seals
-Key materials and components
Glass to Metal Sealing Process
-Step-by-step sealing procedures
-Advanced sealing techniques
-Performance evaluation
Applications of Ceramic Steatite Glass to Metal Seals
SPCERA Ceramic to Metal Seals Inc: Key Company Considerations
-Technical ceramic specifications and parameters
-Material selection and sourcing
-Process optimization
-Quality assurance
Future Trends in Glass to Metal Sealing
-Emerging materials and technologies
-Innovations in hermetic sealing techniques
Conclusion
Fundamentals of Glass to Metal Sealing
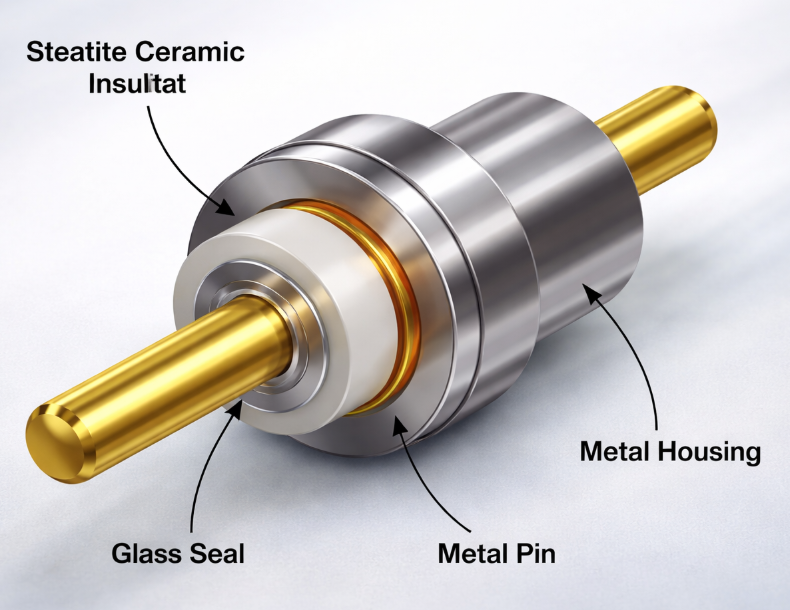
Principles of Glass to Metal Sealing
Glass to metal sealing technology is based on the controlled bonding of glass, ceramic, and metal through carefully matched thermal and mechanical properties. The primary principle involves aligning the coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) between materials to prevent cracking or seal failure during heating and cooling cycles.
In ceramic-enhanced systems, ceramic steatite insulators act as a stable intermediary, providing electrical insulation while supporting mechanical loads. This configuration is particularly valuable in high-voltage and high-temperature environments where conventional polymer insulators fail.
Types of Glass to Metal Seals
Glass to metal seals can be classified into several main categories based on structure and material composition:
1.Conventional Glass-to-Metal Seals
These rely on direct bonding between glass and metal, typically using compression or matched seals. While cost-effective, they may face limitations under extreme thermal cycling.
2.Ceramic to Metal Seals
Ceramic to metal seals introduce a ceramic component—such as steatite—between the glass and metal. This approach enhances insulation performance and improves mechanical reliability.
3.Advantages of Ceramic Steatite Insulator-Based Seals
Ceramic steatite offers excellent dielectric strength, thermal resistance, and dimensional stability. When combined with glass to metal sealing technology, it enables unmatched hermetic seals suitable for precision electronics, connectors, and sensors.
Key Materials and Components
Material selection plays a decisive role in seal performance and lifespan.
1.Common Metals Used
Alloys such as Kovar are widely used due to their thermal expansion compatibility with glass, making them ideal for Kovar glass metal sealing applications.
2.Ceramic Technics Distributors and Sourcing Considerations
Selecting reliable ceramic technics distributors ensures consistent material quality, tight tolerances, and stable supply chains—critical for mass production.
3.Best Steatite Ceramic Bead Price and Quality Factors
Beyond price, factors such as purity, grain structure, density, and bending strength must be evaluated to ensure long-term sealing reliability.
Glass to Metal Sealing Process
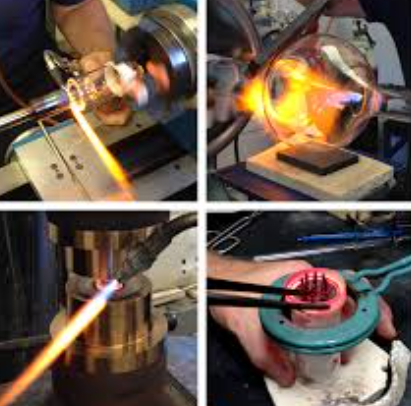

Step-by-Step Sealing Procedures
A typical glass to metal sealing process involves several controlled stages:
Component preparation and cleaning
Glass preform placement and alignment
Heating and controlled melting
Cooling and stress relief
For repair or small-batch applications, liquid glass metallic seal up instructions may be applied. Best practices emphasize controlled heating, proper ventilation, and strict quality checks to avoid micro-leaks or weak bonding.
Safety considerations and quality control are essential, especially when working with high-temperature furnaces and molten glass.
Advanced Sealing Techniques
Modern manufacturers increasingly adopt advanced methods to improve consistency and performance:
1.United Glass to Metal Sealing Methods
These standardized processes combine material science, automation, and precise temperature profiling.
2.Optimization for Unmatched Hermetic Seals
By fine-tuning ceramic geometry, glass composition, and metal surface treatment, manufacturers can achieve leak rates suitable for aerospace and medical-grade applications.
Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluation typically includes:
1.Helium leak testing for hermeticity
2.Thermal shock resistance tests
3.Mechanical strength and fatigue analysis
A performance comparison across seal configurations consistently shows that ceramic steatite glass to metal seals outperform conventional designs in long-term reliability.
Applications of Ceramic Steatite Glass to Metal Seals
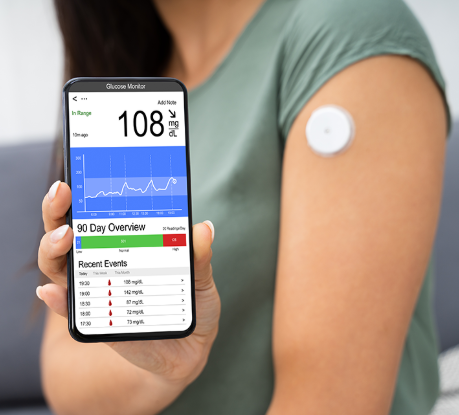

Ceramic steatite glass to metal seals are widely used across multiple industries:
1.Electronics and Electrical Connectors
Ensuring insulation and hermetic sealing in high-voltage connectors and feedthroughs.
2.Aerospace and Defense
Supporting extreme temperature and pressure environments with stable, leak-free seals.
3.Industrial Sensors and Medical Devices
Providing corrosion resistance, electrical isolation, and long service life where safety and precision are paramount.
SPCERA Ceramic to Metal Seals Inc: Key Company Considerations
(h3)Technical Ceramic Specifications and Parameters
From a manufacturing perspective, technical ceramic parameters directly influence sealing performance.
SPCERA Ceramic to Metal Seals Inc focuses on steatite ceramic components optimized for structural and insulating roles in glass to metal sealing systems.
|
Technical Ceramic Specifications and Parameters |
||||||
|
Application |
Code |
Ceramic Composition |
Density |
bending strength |
CTE/10-6(30-300℃) |
Color |
|
Connector structural component |
CM083 |
Steatite Ceramics |
2.85 |
~150MPa |
8.0±0.5 |
White,Light Blue, Green, Grey |
These parameters demonstrate the balance between mechanical strength, thermal compatibility, and electrical insulation required for reliable ceramic to metal seals.
Material Selection and Sourcing
For ceramic-metal sealing companies, material selection is not only a technical issue but also a supply-chain decision. Stable sourcing of steatite ceramics with consistent CTE and density reduces batch variation and improves production yield.
Process Optimization
Process optimization focuses on minimizing stress concentrations, ensuring consistent glass flow, and maintaining dimensional tolerances. Continuous improvement in furnace control and fixture design significantly enhances seal consistency.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance systems typically include:
1.Incoming material inspection
2.In-process dimensional checks
3.Hermeticity and aging tests
These measures are essential to deliver unmatched hermetic seals for high-reliability markets.
Future Trends in Glass to Metal Sealing

Emerging Materials and Technologies
Future developments include advanced ceramic formulations with improved thermal shock resistance and glass compositions tailored for lower processing temperatures.
Innovations in Hermetic Sealing Techniques
Automation, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process control are shaping the next generation of glass to metal sealing technology, enabling higher precision and scalability.
Conclusion
Glass to metal sealing solutions using ceramic steatite insulators represent a mature yet evolving technology. By combining optimized materials, controlled processes, and rigorous quality assurance, manufacturers can achieve unmatched hermetic seals across demanding applications. As material science and manufacturing technologies continue to advance, ceramic-enhanced glass to metal sealing will remain a cornerstone of high-reliability industrial design.






