Understanding Unmatched Hermetic Seals in Glass to Metal Seal Applications
Release time:2025-12-27
Unmatched hermetic seals play a critical role in modern electronic, industrial, and energy applications where reliable airtight performance is required without relying on precisely paired sealing components. Among various hermetic sealing methods, glass to metal seals stand out for their structural stability, thermal compatibility, and long-term reliability. This article explores how unmatched hermetic seals function within glass to metal seal applications, covering sealing principles, design considerations, manufacturing processes, compression sealing structures, integrated assemblies, and recent advances in glass to metal sealing technology.
What is a glass to metal seal?
-What makes unmatched hermetic seals different?
-Why glass to metal seals are ideal for unmatched designs?
Glass to metal sealing process behind unmatched hermetic performance
-Material selection in glass to metal seal design
-Key steps in the glass to metal sealing process
-Process variables affecting hermetic reliability
Glass to metal compression seal solutions
-How glass to metal compression seals work?
-Typical applications of compression seals
United glass to metal sealing for complex assemblies
-What is united glass to metal sealing?
-Advantages for multi-pin and custom feedthrough designs
Advances in glass to metal sealing technology
-Technology trends in hermetic sealing
-Future directions for unmatched hermetic seals
What Is a Glass to Metal Seal?
What Makes Unmatched Hermetic Seals Different?
Unmatched hermetic seals refer to sealing solutions that do not depend on precisely machined, one-to-one matched mating parts to achieve airtight integrity. Instead of relying on paired sealing surfaces, unmatched hermetic seals achieve hermeticity through material bonding, structural stress control, and controlled sealing processes.
In contrast to matched sealing systems—where housings and lids are processed and validated as a set—unmatched hermetic seals offer greater design flexibility, interchangeability, and scalability. This makes them particularly suitable for applications requiring standardized components, modular assembly, or high-volume manufacturing without sacrificing sealing performance.
Why Glass to Metal Seals Are Ideal for Unmatched Designs
Glass to metal seals are especially well-suited for unmatched hermetic sealing because the sealing interface itself provides the airtight barrier. By bonding glass directly to metal, the seal becomes an integral structural component rather than a dependent interface between two matched parts.
This approach enables excellent resistance to gas leakage, temperature cycling, vibration, and long-term aging. As a result, glass to metal seals are widely used in unmatched hermetic seal designs for sensors, electronic feedthroughs, batteries, relays, and vacuum devices.
Glass to Metal Sealing Process Behind Unmatched Hermetic Performance
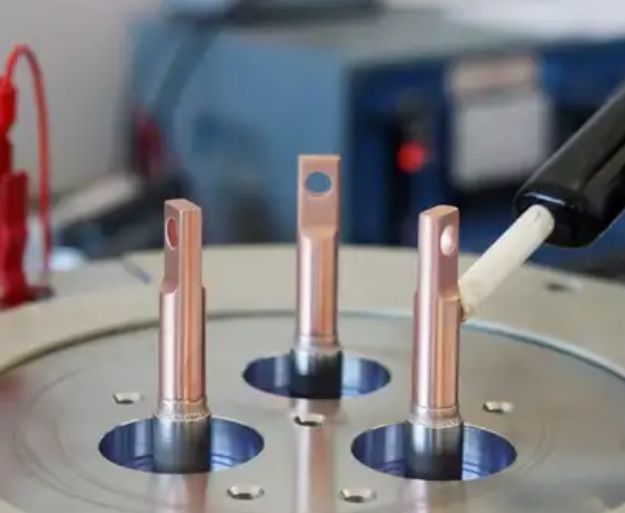

Material Selection in Glass to Metal Seal Design
Material compatibility is a fundamental factor in glass to metal seal design. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the glass must be carefully matched—or intentionally offset—to the metal used, depending on the sealing strategy. Common metals include Kovar, stainless steel, and nickel alloys, while sealing glass compositions are selected to maintain mechanical integrity and electrical insulation.
In unmatched hermetic seals, material selection focuses on achieving stable stress distribution rather than tight dimensional matching. This allows the seal to perform consistently across different assemblies and operating conditions.
Key Steps in the Glass to Metal Sealing Process
The glass to metal sealing process typically involves several controlled stages. First, metal components and glass preforms are thoroughly cleaned to ensure proper wetting and bonding. The assembly is then heated in a controlled atmosphere until the glass softens and flows against the metal surface.
As the assembly cools, the glass solidifies and bonds permanently to the metal, forming a hermetic interface. Precise temperature control during heating and cooling is essential to prevent cracking, void formation, or residual stress that could compromise sealing performance.
Process Variables Affecting Hermetic Reliability
Several process variables directly affect the reliability of unmatched hermetic seals. These include heating rate, peak sealing temperature, cooling speed, and atmospheric conditions. Improper control can introduce microcracks, trapped gases, or uneven stress distribution.
Advanced manufacturing processes use precise thermal profiles and monitoring systems to ensure consistent sealing quality, enabling glass to metal seals to meet stringent leak rate and durability requirements.
Glass to Metal Compression Seal Solutions
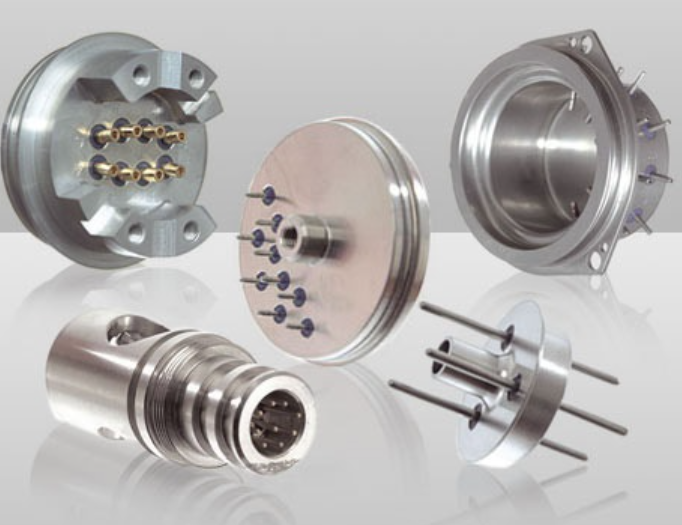

How Glass to Metal Compression Seals Work
A glass to metal compression seal is a specific sealing structure in which the metal housing contracts more than the glass during cooling, placing the glass under compressive stress. This compression enhances mechanical strength and significantly improves hermetic reliability over time.
Compression seals are particularly advantageous in unmatched hermetic seal designs because they are less sensitive to dimensional variations and external mechanical loads.
Typical Applications of Compression Seals
Glass to metal compression seals are commonly used in high-reliability environments such as aerospace electronics, automotive sensors, industrial instrumentation, and energy storage systems. Their ability to maintain airtight performance under pressure, vibration, and thermal cycling makes them a preferred choice for unmatched hermetic sealing in demanding applications.
United Glass to Metal Sealing for Complex Assemblies

What Is United Glass to Metal Sealing?
United glass to metal sealing refers to an integrated sealing approach where multiple functional elements—such as pins, housings, and insulating glass—are combined into a single hermetic assembly. Instead of sealing each component separately, the entire structure is sealed as one unified unit.
This approach simplifies assembly while maintaining consistent hermetic performance across multiple interfaces.
Advantages for Multi-Pin and Custom Feedthrough Designs
In unmatched hermetic seals, united glass to metal sealing offers clear advantages for multi-pin feedthroughs and custom configurations. It reduces assembly steps, improves alignment accuracy, and enhances long-term sealing stability.
Such designs are widely used in electronic packaging, power devices, and sensor systems where space efficiency and reliability are critical.
Advances in Glass to Metal Sealing Technology

Technology Trends in Hermetic Sealing
Recent advances in glass to metal sealing technology focus on improved glass formulations, optimized metal surface treatments, and enhanced process control. These developments enable higher sealing consistency, improved resistance to harsh environments, and better performance in miniaturized components.
Automation and digital monitoring are also increasingly used to reduce process variability and improve production efficiency.
Future Directions for Unmatched Hermetic Seals
As electronic and industrial systems continue to evolve, unmatched hermetic seals are expected to play an even greater role. Future developments will emphasize higher integration, improved material sustainability, and enhanced performance under extreme conditions.
With continued innovation in glass to metal sealing technology, unmatched hermetic seals will remain a reliable and flexible solution for a wide range of hermetic sealing applications.






