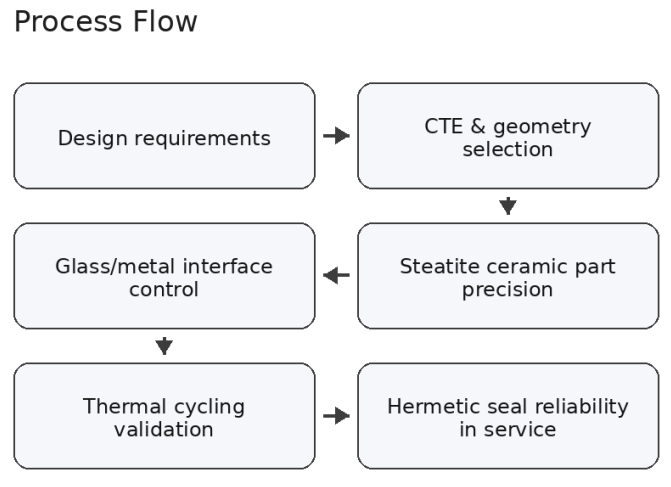
How Steatite Ceramic Enhances the Reliability of Ceramic to Metal Seals?
Release time:2026-01-23
Reliable ceramic to metal seals are critical wherever leakage, electrical failure, or thermal cycling damage can compromise performance. As a widely used material in technical ceramics, steatite ceramic supports sealing reliability through a practical mix of low thermal expansion, excellent electrical insulation, thermal stability, and robust strength. These attributes help reduce thermal mismatch stress, protect interfaces, and improve long-term hermetic seal performance in demanding service conditions. This article explains why steatite ceramic is well suited for ceramic-to-metal sealing systems, how it supports glass-to-metal sealing architectures, and how to evaluate ceramic to metal seals suppliers with clear technical criteria and documentation.
Introduction to Steatite Ceramic in Ceramic to Metal Seals
-Why reliability matters for ceramic to metal seals?
-What makes steatite ceramic relevant to sealing reliability?
-How this guide is structured for engineers and procurement teams?
Talc Ceramics as a Core Technical Ceramic Material
-Steatite ceramic within the technical ceramics category
-Key steatite ceramic properties that influence seal reliability
-Engineered for precision in critical sealing geometries
Ceramic to Metal Seals for High-Reliability Applications
-What ceramic to metal seals are and how they work
-Defining hermetic seal performance in practical terms
-Application areas that depend on long-term reliability
Steatite Ceramic in Glass to Metal Sealing Technology
-How glass to metal sealing relates to ceramic to metal seals
-Why low thermal expansion stabilizes glass-to-metal sealing interfaces
-Practical process checkpoints that protect sealing outcomes、
Steatite Ceramic as a Reliable Solution for Hermetic Seals
-What makes a ceramic material “hermetic-ready”
-How steatite ceramic reduces leak risk over lifecycle conditions
Ceramic to Metal Seals Suppliers Selection Guide
-What to look for in ceramic to metal seals suppliers
-Supplier scorecard for procurement and engineering alignment
-RFQ checklist to speed up quoting and reduce redesign loops
Introduction to Steatite Ceramic in Ceramic to Metal Seals
Why reliability matters for ceramic to metal seals?
In many industrial and electronic systems, a seal failure is not a minor defect—it can be a mission-ending event. Ceramic to metal seals often serve multiple functions at once: they provide a structural joint, deliver electrical insulation, and isolate internal components from moisture, gases, or pressure differentials. When reliability is insufficient, several failure modes can appear: microcracks from thermal cycling, interface separation at the joint, insulation degradation, or a gradual increase in leak rate. Any of these can lead to loss of hermetic seal
Reliability is especially important because ceramic-to-metal assemblies frequently operate under conditions that amplify stress: repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles, vibration, mechanical shock during handling or installation, and long-term exposure to humidity or corrosive media. A design that looks robust at room temperature can become vulnerable after hundreds or thousands of temperature cycles. For that reason, selecting the right ceramic material—and controlling geometry, tolerances, and interface quality—plays a central role in consistent sealing performance.
What makes steatite ceramic relevant to sealing reliability?
Steatite ceramic is a proven choice within the technical ceramics family because it offers a balanced set of properties that map directly to sealing reliability. One of its most valuable advantages is low thermal expansion
Steatite ceramic also delivers excellent electrical insulation, which is essential in feedthroughs, connectors, and insulating components where leakage current or dielectric breakdown can cause functional failure even before a seal leaks. Its thermal stability helps maintain consistent behavior at operating temperatures, supporting repeatable performance across service life. Finally, good mechanical strength and manufacturability make it suitable for parts that must survive assembly loads and handling while maintaining tight dimensional control—an often overlooked requirement for high-quality sealing interfaces.
How this guide is structured for engineers and procurement teams?
This guide follows a practical sequence. It first explains why ceramic-to-metal seal reliability matters and how steatite ceramic fits into the broader technical ceramics landscape. It then links specific steatite ceramic properties to reliability outcomes using a clear mapping table. Next, it summarizes how ceramic-to-metal seals function in high-reliability applications and defines hermetic seal performance in practical terms. After that, it shows how steatite ceramic contributes in glass to metal sealing architectures and highlights process checkpoints that protect sealing outcomes. Finally, it offers a supplier selection scorecard and an RFQ checklist to speed quoting and reduce redesign loops.
Talc Ceramics as a Core Technical Ceramic Material

Steatite ceramic within the technical ceramics category
The technical ceramics market serves applications that demand repeatable performance beyond what standard materials can deliver—especially where electrical insulation, thermal stability, and dimensional precision are required. Steatite ceramic occupies a practical position within this category. It is widely recognized for consistent insulation performance and for helping engineers manage thermal stress through relatively low expansion behavior. For many sealing designs, steatite ceramic becomes attractive because it balances performance with manufacturability and stable supply availability, enabling scalable production without sacrificing reliability targets.
In comparison with other ceramics used in sealed assemblies, steatite is often chosen when the system requires strong insulation, good thermal behavior, and cost-effective, repeatable part production. This combination makes it suitable for connector-style geometries, feedthroughs, and insulating bodies used across industrial electronics, sensing, and high-voltage components.
Key steatite ceramic properties that influence seal reliability
Seal reliability is rarely determined by one parameter alone. It is the combined effect of thermal, electrical, mechanical, and manufacturing-related characteristics. Steatite ceramic supports reliability through:
1.Thermal mismatch control: low thermal expansion reduces stress at the ceramic-metal interface during heating and cooling.
2.Electrical stability: excellent insulation reduces the risk of leakage current and dielectric breakdown, especially in compact or high-voltage designs.
3.High-temperature consistency: thermal stability helps maintain predictable behavior under operating temperatures.
4.Mechanical robustness: strength improves resistance to handling damage, assembly loads, and service vibration.
5.Interface-friendly manufacturability: precision manufacturing improves fit-up and interface uniformity, reducing the chance of micro-leak pathways.
Engineered for precision in critical sealing geometries
Many ceramic-to-metal seal failures begin not in the bulk material, but at the interface—where stress concentrates and defects are most damaging. Precision matters because even small deviations in geometry can create local gaps, uneven contact, or stress risers that turn into crack initiation points. A steatite ceramic component with controlled dimensions and surface quality supports more uniform joining behavior, whether the system relies on brazing, metallization, or glass-based sealing elements.
Precision also notes a practical procurement reality: the best material cannot compensate for uncontrolled tolerance stack-up. If the ceramic body varies across batches, the joint process becomes less predictable, which can increase scrap rates and reliability risk. For this reason, “precision manufacturability” is not a secondary detail—it is a reliability driver.
Table 1 — Property-to-Reliability Mapping
|
Steatite Ceramic Property |
Why It Matters in Ceramic to Metal Seals |
Reliability Outcome |
|
Low thermal expansion |
Reduces thermal mismatch stress during heating/cooling |
Fewer cracks, stronger interfaces |
|
Excellent electrical insulation |
Prevents leakage current and dielectric breakdown |
Stable electrical performance over life |
|
Thermal stability |
Maintains properties under operating temperatures |
Consistent hermetic seal integrity |
|
Mechanical strength |
Resists handling, assembly stress, vibration |
Lower risk of mechanical failure |
|
Precision manufacturability |
Improves fit-up and interface uniformity |
Reduced micro-leak pathways |
Ceramic to Metal Seals for High-Reliability Applications

What ceramic to metal seals are and how they work
A ceramic to metal seal
Well-designed ceramic-to-metal seals manage stress through material selection and geometry. They also reduce defect sensitivity by controlling surfaces, edges, and the microstructure of the ceramic body. When the ceramic is dense and the interface is uniform, the system becomes far less likely to develop leak paths under cycling.
Defining hermetic seal performance in practical terms
A hermetic seal should be defined with measurable criteria that reflect real operating conditions. In many programs, this includes:
1.Leak testing to verify initial tightness and identify gross leaks early.
2.Thermal cycling validation to confirm the joint survives repeated expansion and contraction.
3.Environmental checks when required (humidity exposure, corrosion media, or pressure/vacuum conditions).
4.Electrical verification for insulated assemblies (insulation resistance and withstand testing, depending on application).
If your goal is “unmatched hermetic seals,” the most effective approach is to treat it as a performance target that must be verified through consistent testing and documentation. In procurement terms, unmatched performance is a combination of material consistency, precision manufacturing, and validated sealing outcomes—not a single design claim.
Application areas that depend on long-term reliability
Ceramic-to-metal seals are widely used in applications where long service life and stable performance are critical. Examples include sensor packaging, industrial instrumentation, vacuum systems, rugged connectors, electrical feedthroughs, and high-voltage insulation components. These applications share the same reliability pressures: thermal cycling, mechanical vibration, and environmental exposure. Steatite ceramic’s combination of low thermal expansion and strong insulation makes it well noted for such use cases, especially where consistent geometry and robust sealing interfaces are required.
Steatite Ceramic in Glass to Metal Sealing Technology

How glass to metal sealing relates to ceramic to metal seals
In many sealing systems, glass to metal sealing is used to create a tight barrier, while a ceramic component provides electrical insulation and structural stability. This is common in assemblies where electrical conductors must pass through a sealed boundary while maintaining insulation. In these architectures, the ceramic body influences how stresses are distributed and how stable the overall geometry remains during temperature changes.
Steatite ceramic can support these systems by providing stable insulation and helping reduce thermal mismatch effects in the broader assembly. When geometry and material pairing are designed thoughtfully, steatite contributes to a more stable interface environment—supporting consistent sealing behavior.
Why low thermal expansion stabilizes glass-to-metal sealing interfaces
Thermal cycling remains one of the most frequent stressors for sealing interfaces. If expansion behavior among materials differs substantially, stress can concentrate in narrow regions and lead to microcracks. Once microcracks form, leak rates can increase over time, particularly if cycling continues. Steatite’s low thermal expansion helps reduce stress amplification and can improve stability at and around the interface—supporting longer-lasting hermetic seal performance.
Practical process checkpoints that protect sealing outcomes
A reliable sealing outcome is not only about choosing steatite ceramic—it is also about controlling the process steps that affect defects and interface quality. Key checkpoints include:
1.Ceramic density and defect control: minimize porosity and microcrack risk.
2.Surface preparation and cleanliness: remove contaminants that can disrupt bonding or create leakage paths.
3.Dimensional control: ensure consistent fit-up and predictable interface contact.
4.Thermal profile control: manage heating and cooling to reduce residual stress.
5.Validation testing: confirm leak rate and stability after thermal cycling.
Steatite Ceramic as a Reliable Solution for Hermetic Seals
What makes a ceramic material “hermetic-ready”
A ceramic is “hermetic-ready” when its bulk body is dense, its porosity is controlled, its surface quality is suitable for consistent joining, and its geometry can be produced reliably at scale. In practice, this means minimizing connected porosity, preventing edge chipping in sealing zones, and maintaining stable dimensions that support uniform interfaces. Because leak paths often originate at defects or irregularities, the combination of microstructure control and precision finishing is critical.
How steatite ceramic reduces leak risk over lifecycle conditions
Steatite ceramic helps reduce leak risk across the full product lifecycle. During assembly, mechanical strength and stable geometry reduce damage risk and improve joint repeatability. During thermal cycling, low thermal expansion helps reduce crack initiation and slows fatigue mechanisms at the interface. During service, thermal stability supports consistent behavior at operating temperatures, while excellent electrical insulation helps prevent electrical degradation mechanisms that can accelerate failure in compact designs. Together, these advantages support stable hermetic seal performance and help maintain reliability even as conditions fluctuate over time.
Ceramic to Metal Seals Suppliers Selection Guide

What to look for in ceramic to metal seals suppliers
Choosing the right ceramic to metal seals suppliers can be as important as selecting the right ceramic. A strong supplier should demonstrate:
1.consistent steatite ceramic properties across lots,
2.precision capability for critical sealing geometries,
3.clear hermetic seal validation methods,
4.reliability test support (thermal cycling, aging plans when needed),
5.engineering collaboration for design iteration and DFM alignment.
Reliable suppliers also provide documentation that supports repeatability: COA records, inspection reports, traceability, and test plans aligned to your acceptance criteria.
Supplier scorecard for procurement and engineering alignment
Table2— Supplier Evaluation Scorecard
|
Evaluation Area |
Questions to Ask |
Evidence to Request |
|
Material consistency |
How do you control lot-to-lot variation? |
COA, key metrics, traceability |
|
Precision capability |
What tolerances and surface finishes are typical? |
Inspection reports, capability notes |
|
Hermetic seal validation |
What leak tests do you run and how often? |
Test method, criteria, sample plans |
|
Reliability testing |
Do you support thermal cycling or aging tests? |
Test plans and representative results |
|
Engineering support |
Can you support design iteration and DFM? |
Project workflow, timelines |
RFQ checklist to speed up quoting and reduce redesign loops
A complete RFQ reduces back-and-forth and helps suppliers quote accurately. Include: operating temperature range; expected thermal cycling conditions; target leak rate and preferred leak test method; metal selection and interface approach (brazing, metallization, glass-based sealing, or hybrid); drawings with critical dimensions, tolerances, and surface requirements; environmental conditions (humidity, corrosion media, pressure/vacuum); annual volume forecasts; and documentation expectations (COA, traceability, inspection and test reports). With these inputs, suppliers can propose the best-fit steatite ceramic solution, align process controls to your reliability targets, and support consistent sealing outcomes.
In Conclusion
Steatite ceramic strengthens the reliability of ceramic to metal seals by addressing the factors that most often cause leakage and premature failure—thermal mismatch stress, interface instability, and inconsistent insulation performance. With low thermal expansion, excellent electrical insulation, and stable behavior under thermal cycling, steatite ceramic helps protect joint integrity and sustain hermetic seal performance in demanding applications. The best results come from combining the right material choice with precision-controlled geometries, disciplined interface processing, and verification through leak testing and thermal cycling. When evaluating ceramic to metal seals suppliers, prioritize documented material consistency, proven precision capability, and validated sealing evidence to achieve repeatable, high-confidence outcomes—up to and including truly “unmatched hermetic seals” supported by data.







